
SUMMARY
Imagine if you were able to understand what influences the brain of your target audience before releasing content and campaigns. What questions would you want to be answered before spending money on advertisement? While this may seem impossible, neuroscience has virtually turned this into a reality. Experts aptly term the process of stimulating a buyer’s mind to expend money on what you desire him/her to as — NeuroMarketing. Till date, it is the most improvised form of marketing and the takers are multiplying by the day.In this blog post you will cover:
- What Big Data Doesn’t Show you
- Why 90% of online and offline product fell within the first year
- Why some focus groups can be severely flawed (infographic)
- How emotion is the key driver in decision making
- An introduction to Neuromarketing
- 4 Neuromarketing Great Case Studies
- Neuro-Content Marketing: Applications of neuroscience into content marketing
An Introduction to Neuro-Content Marketing
The landscape of digital consumer behaviour has undergone tectonic changes. It is the result of unprecedented marketing strategies combined with technology. The strategies devised by industry experts give us insights into the consumer brain. It further makes it possible for us to create content and ads that target their needs and aspirations alike.
There are multiple mediums to engage with online audience. Marketing and sharing is easier than ever before and, of course, we are all aware of the robust analytics “Big Data” that can be obtained in real time. These opportunities, however, come with huge challenges.
While we have access to a ‘crap-ton’ of information, it is hard for companies to keep up with the and amount of data changes. In this case, it is a challenge for brands to come up with actionable marketing strategies. How do you plan your marketing content? How do you sieve the relevant from the redundant?
Why 90% of Products Still Fail
Let’s take a look at the history of marketing industry…
Traditionally, marketing was executed on the merit of data collected from focus groups. The survey gave industry experts an idea of what consumers wanted and would do to obtain a product or service.
Most companies across the world have at one point formed focus groups for market research. It enabled them to know people’s opinion on a product or a campaign. Having a better understanding of what consumers would buy and respond to helped them devise a marketing strategy accordingly.
A lot has changed in the last decade. In present times, we optimally use the traditional media to sell our products in physical stores, on television, and even market these through conventional means. Then, we have the platform of the internet, which has opened a new world of possibilities of selling and collecting consumer research through “Big Data”.

A plethora of tools are used to measure the success of marketing efforts. We’ve come a long way from the focus-group scenario of asking people their choices and responses to now being able to watch and analyze transactional data in real time.
But, here we also have a catch! Even after conducting market research with focus groups and analytics in place, why do 80-95% of products (physical and digital) fail within the first year of hitting the shelves?
Roughly 21,000 new brands are introduced worldwide per year, yet history tells us that more than 90% of them are gone from the shelf a year later. – Martin Lindstrom
Failure strikes because majority of people don’t know exactly why they make the decisions they do. They also don’t know how to articulate what they want and why they want it. In marketing’s traditional focus groups, many individuals can be swayed by the opinions of others. What is one person’s right is not necessarily correct.

In conventional market research practices, if this behavior exists, how accurate do you think the analyses are? Unfortunately, our content marketing and advertisements are developed after conclusions are drawn from this presumably accurate data, and thus millions of dollars go down the drain.
Through digital platforms, Big Data is allowing us to obtain information in an entirely new way. Data collection isn’t dependent on focus groups, it is now available through expansive digital means.
Although Big Data has helped us tremendously, there is still a big gap in the data we obtain digitally or through focus groups and how we can by using it provide an efficient marketing strategy that truly speaks of what consumers want.
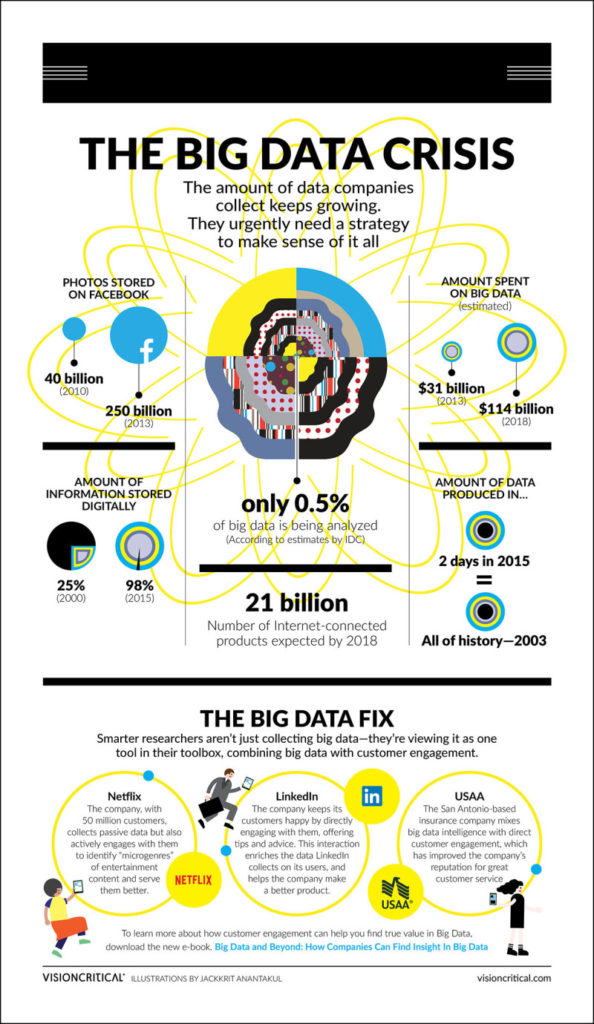
The infographic below titled “Big Data Crisis” shows how the amount of data, which companies collect keeps growing, and the challenge of how to make sense of it keeps growing as well.
Smarter researchers aren’t just collecting big data —they’re viewing it as one tool in their toolbox, combining big data with customer engagement.
Deeper Digital Consumer Understanding
If you plan to use information acquired from Big Data just to market, you will only get limited insight into the consumer behavior pattern. When marketing to your target audience, keep in mind that majority of buying decisions are rational and 90% unconscious.
Big Data has the inability to capture subconscious / emotional data, which drives consumer-buying decisions and engagement. When sales are made, they are based on only 20% logic and 80% emotion. This is known as the Sales Influence Equation.
If you take a closer look above, you will notice, even companies like Netflix, LinkedIn and USAA still need to make direct contact with their audience to get a better understanding of what they want.

Emotions Dictate Your Decisions & Purchases
Without emotion, decisions are literally impossible to make. Emotion is the leading force that drives people to make decisions. You may think that logic is the determining factor, (especially in business decisions), but the buck stops at emotion. Emotion is what brings context to your decisions and how these will impact you. Logic is purely an act of measuring complexity.
Here is an Example
Elliot was a successful attorney until he underwent surgery to remove a tumor from his brain. This unfortunately seemed to have destroyed a part of his personality. The very energetic man turned into someone who could no longer take decisions.
He was unable to write anything, because he could not decide which pen to use. He wanted to listen to the radio but could not find a station, he planned to tidy his desk, but did not know how.
Elliot’s IQ remained unchanged, yet he was no longer able to deal with his daily routine. After being introduced to António Rosa Damásio, a renowned psychiatrist, it was diagnosed that Elliot was completely emotionally stunted. He wasn’t sad, frustrated or happy, everything felt the same to Elliot. Damásio suspected this was the reason why Elliot could no longer take any decisions.
Minimise Marketing Investment Risk
Strategic marketing is the key to a thriving business venture. Companies which don’t market effectively run a high risk of leaving lots of money on the table. When companies pay attention to marketing, it begins to earn qualitative and quantitative advantage against their competitors as well as the previous year’s financial projections.
It is unfortunate that market-research exercises, such as focus groups and Big Data mining are beneficial but still these pose a risk to marketing investment. A solution to minimise risk and bridge the gap of emotional data research, major companies have turned to the billion-dollar industry of brain science — Neuromarketing.
Theories behind neuromarketing were first explored by marketing professor Gerry Zaltman in the 1990s. Zaltman and his associates were employed by organizations, such as Coca Cola ltd, to investigate brain scans and observe neural activity of consumers.
What is Neuromarketing
Neuromarketing is the application of neuroscience to marketing. Neuromarketing includes the direct use of brain imaging, scanning, or other brain activity measurement technology to measure the subject’s response to specific products, packaging, advertising, or other marketing elements.
In some cases, the brain responses measured by these techniques may not be consciously perceived by the subject; hence, this data may be more revealing than self-reporting on surveys, in focus groups, etc.
Neuromarketing also includes the use of neuroscience research in marketing. For example, using MRI or other techniques, researchers may find that a particular stimulus triggers a consistent response in the brain of test subjects, and that this response is correlated with desired behaviors (e.g., trying something new).
A marketing campaign that works on a particular stimulus, hoping to create specific behaviors is an example of neuromarketing, even though no physical testing of subjects is conducted for the campaign.
5 Neuromarketing Case Studies
Here are a few case studies of how multinational companies applied neuroscience to marketing in the past. You may also be familiar with some of the content that was tested to ensure emotional engagement.
1. Company: Mercedes Benz
Mercedes Benz used neuromarketing for a campaign, in which the front of cars were simulating human faces, linking directly to the pleasure center of the brain.
Result: Sales increased 12% in the first quarter as a result.
2. Company: PepsiCO’s Frito-Lay
Frito-Lay conducted a test which was through a focus group as well as using Neuromarketing EEG technology. The clip of Cheetos ad shows a woman taking revenge on someone in a Laundromat by putting the orange snack food in a dryer full of white clothes.
Participants in the focus group said they didn’t like the prank, but when silent EEG test were ran, it showed brain activity suggesting that the women loved the ad. Because participants didn’t want to look too mean-spirited to other focus group members, they were not truthful about their opinion.
Result: The snack-food marketer aired the prank ad as a result of data from EEG testing
3. Company: Yahoo

Yahoo had a 60-second television clip that features happy, dancing people around the world. Before spending the money on ad, Yahoo ran it by EEG-cap-wearing consumers.
The brain waves in consumer targets showed stimulation in the limbic system and frontal cortices of their brains, where memory and emotional thought occurs.
Result: The successful ad, was part of Yahoo’s $100 million branding campaign, rolled out to prime-time cable TV and online.
4. Company: Coca Cola
This TVC commands consistent and sustained parietal response. Clear peaks occur when the insects start moving the bottle, when they open it, and when the fake bottle of Coke disperses. This is a highly visual ad, with strong visual cortex activation.
Result: Ranked #2 during the Super Bowl XLIII Ad Study is “Heist” by Coke.
5. Company: Microsoft
Microsoft is using EEG data to demonstrate how engaged gamers are when they use an Xbox. Working with EmSense, Microsoft put EEG caps on gamers and showed them ads on the video game system. It tracked which parts of the brain were stimulated by the ads. Ads that excite several parts of the brain are supposed to make viewers more likely to go out and buy the product advertised, says Michael E. Smith, neuroscientist at NeuroFocus. Microsoft’s goal: Get advertisers to buy 30-second spots on Xbox games. The company is footing the bill to test ads for six marketers.
Driving Content Marketing with Neuroscience

Firms and business houses are increasingly betting on content marketing to drive their promotional initiatives.
Traditional advertising mediums such as television, direct mail are becoming obsolete due to the instant access of information online.
Wikipedia defines content marketing as a form of marketing that focuses on creating, publishing and distributing content for a targeted audience online. It is often used by businesses to serve the following purposes
- Expand the user base
- Diversify the user base
- Establish or Increase online sales
- Increase brand awareness or credibility
- Create an online community of users
Content Marketing is expected to grow in a $300 Billion Industry by 2019. According to the Content Marketing Institute, the industry is considered “Today’s Marketing”.
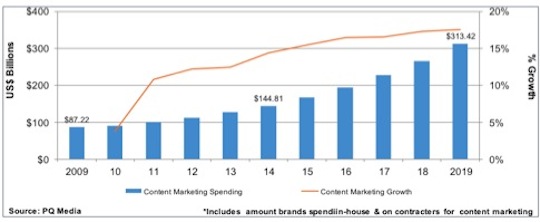
Many major brands are spending upwards of $1.5 million per year for content marketing as it provides a unique way to tell their story and create a space for them in the market. It also enables them to track their return on investment.
Though the content marketing strategists are making brands earn profits, some CEOs and marketers feel they aren’t getting the maximum ROI of content marketing.
It is being believed that some money is still being left on the table. Companies do not know how to engage visitors with the content they create as well as the techniques to convert visitors to leads, customers or fans.
There are great analytics tools that help companies view engagement, however, neuromarketing is a tool that can ensure every dollar invested in the content marketing is accounted for. The marketers use research to predict engagement effectiveness of your target audience before the campaigns are released.


Applications
The nucleus accumbens, is known as “the pleasure center”of the brain. When we receive signal about situations and objects that provide us reward and pleasure ie: (eating snack foods, having sex, etc.), our brains activate dopamine. The electrical impulses in this area of the brain can be measured by tools such as EEG and fMRIs. When content is tested for engagement, this is one of the primary areas that neuroscientist look for activation.
Neuro-Content Marketing is performed through tools such as EEG, Eye Track & fMRI. There are three primary categories which are measured: Attention, emotion and memory.
Though neuromarketing and content marketing have both been around for sometime, there are not many cases where these processes have been combined and their combination can work magic.
Neuro-content marketing should be used for high-end campaigns in order to minimize the investment risk of marketing. This data paired with Big Data is very powerful.
Here’s suggestion few mediums through which Neuro-content marketing can be made accessible to target audience.
1. Video
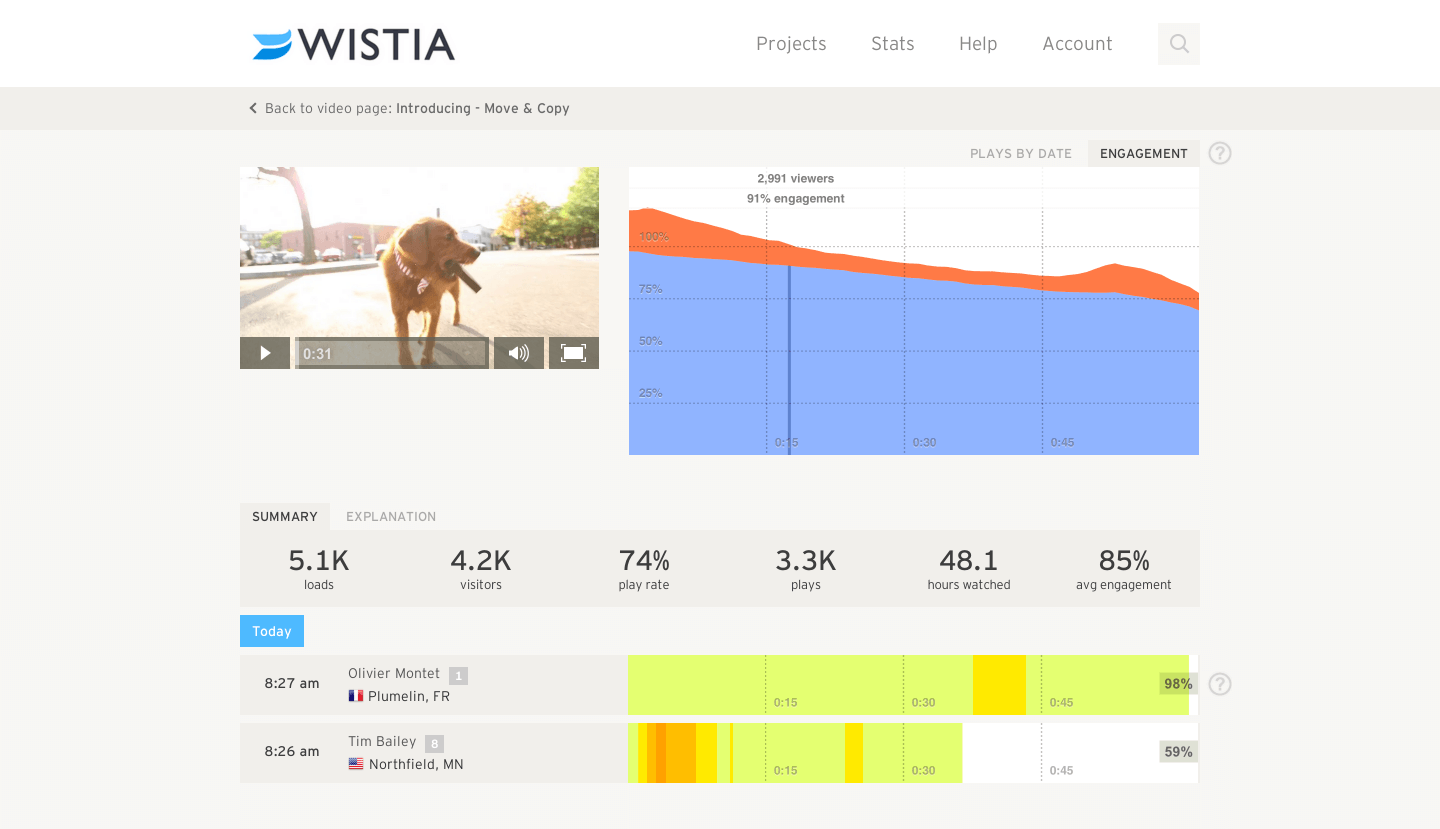
Video has become one of the most effective mediums to build rapport and trust, while also enhancing brand perception and influence. Video drive and educate customers as they navigate through your marketing funnels.
To spend money on promoting videos that do not convert and engage can prove to be a very costly exercise. To safeguard marketing expenditure, neuroscientists conduct comparative testing against videos that already proved to have a high-emotional engagement ratio.
2. Web Lead Page Funnels, Ecommerce & Designs
There are some great products out there such as crazy egg and x, which allow us to track where the mouse clicks, what makes the eyes wander and how people feel about content or products.
To find more information on how Neuromarketing can be applied to Content Marketing, please continue to follow us for constant insights.
